Chain Halt Troubleshooting
Chain Halt Troubleshooting
Understanding Chain Halts
Definition and Causes
Chain halts are critical events in blockchain networks that occur when validators fail to reach consensus. In our Cosmos SDK-based chain, consensus requires agreement from at least 67% of the voting power to produce new blocks.
These halts typically arise from non-deterministic scenarios, where different validators have conflicting views of the blockchain state. Common causes include:
- Inconsistent application of state transition rules
- Divergent interpretations of transaction data
- Synchronization issues between nodes
- Software bugs leading to inconsistent state calculations
Impact on Network
Chain halts can have severe consequences for the network:
- Transaction processing comes to a standstill
- Users cannot interact with the blockchain
- Potential loss of confidence in the network's reliability
- Financial implications for stakeholders and users
Given these impacts, swift and effective troubleshooting is crucial to maintain network health and user trust.
Troubleshooting Process
Step 1: Identifying the Issue
When a chain halt occurs, the first step is to identify the specific error message or symptom. A common indicator is the wrong Block.Header.AppHash error, which suggests a mismatch in the calculated state between nodes.
Step 2: Collecting Node Data
To investigate the discrepancy:
- Locate the database directory on the affected node (typically
$HOME/.poktroll/data). - Obtain the same directory from a healthy full node or one with a different
Block.Header.AppHash. - Ensure you have appropriate permissions to access and copy this data.
Step 3: Analyzing Discrepancies
Utilize the iavl-tree-diff tool to compare the two database snapshots:
- Clone the repository containing the tool.
- Follow the tool's documentation to set up and run the comparison.
- The tool will highlight specific areas where the two nodes' states diverge.
Step 4: Decoding and Interpreting Data
The blockchain data is stored in protobuf format, encoded as hexadecimal.
To interpret this data:
- Use CyberChef: a versatile data manipulation tool.
- Input the hexadecimal data into CyberChef.
- Apply the "From Hex" operation followed by "Protobuf Decode" to reveal the human-readable content.
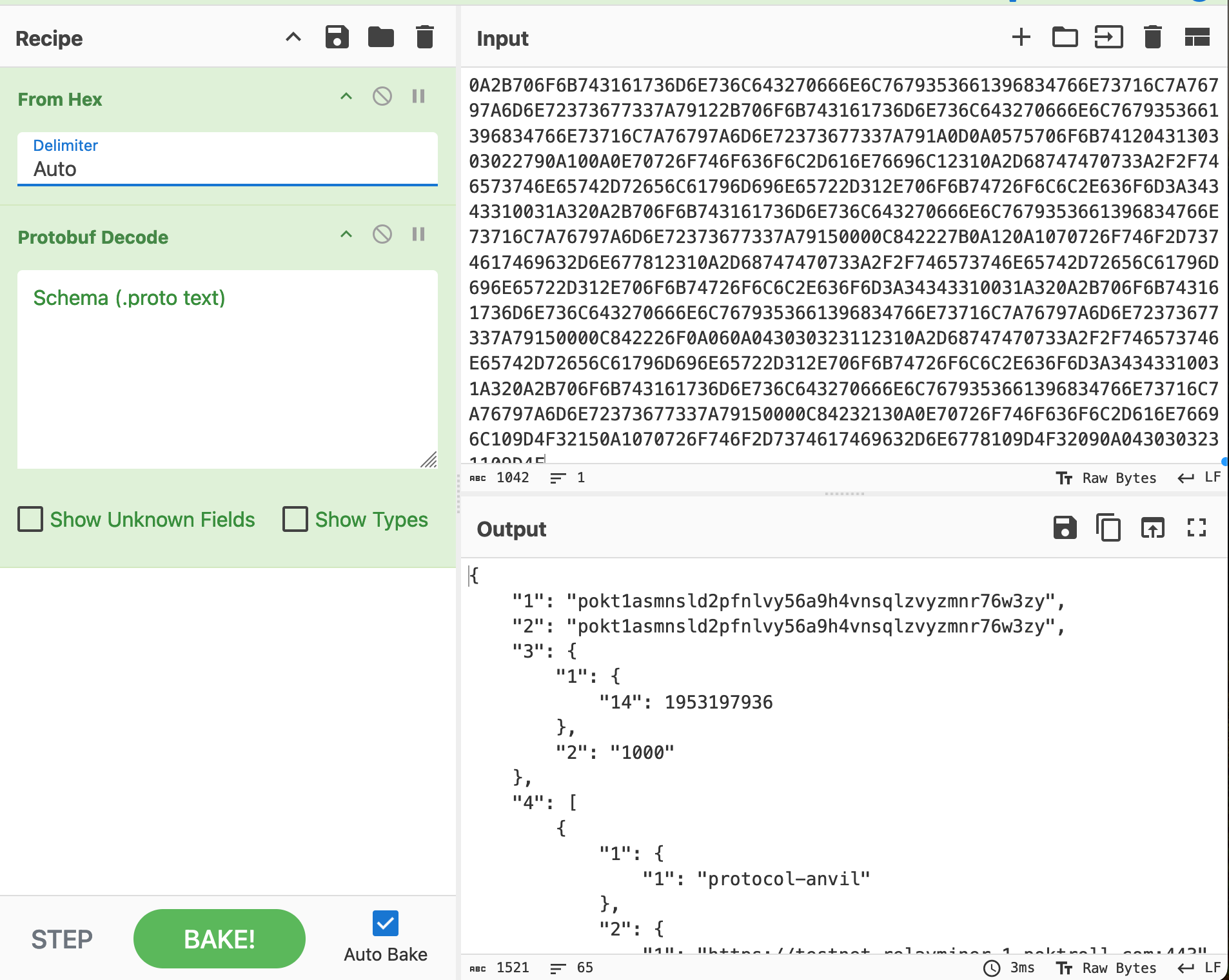
Step 5: Comparing Records
After decoding, compare the data from both nodes:
- Use a diff tool (CyberChef can also be used for this purpose).
- Identify specific fields or values that differ between the two records.
- Pay close attention to timestamps, numerical values, and complex data structures.
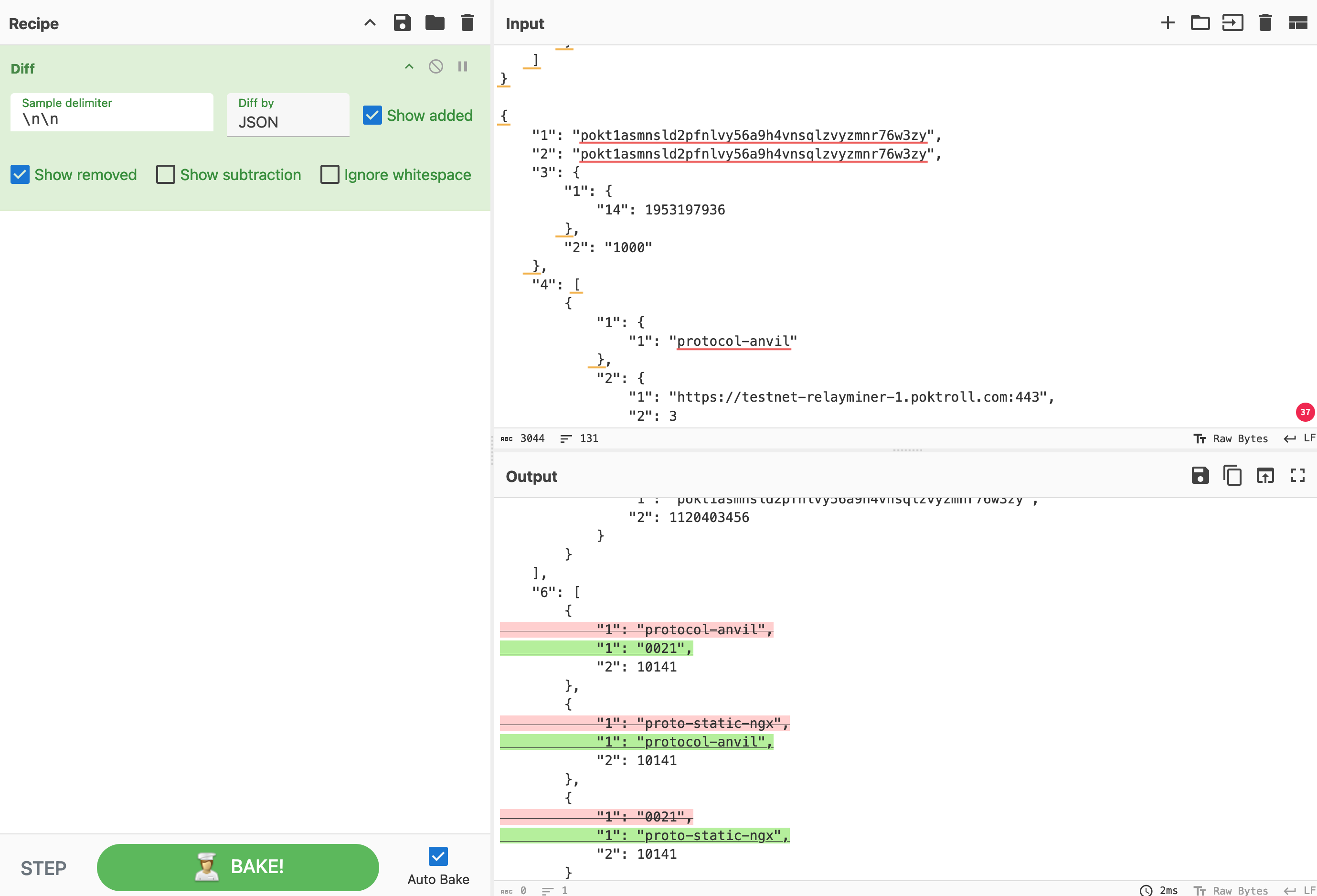
The image above illustrates a difference in the JSON representation of an object, which is likely the root cause of the non-deterministic state breaking consensus between nodes.
Step 6: Investigation and Resolution
Based on the identified discrepancies:
- Investigate the underlying cause of the difference (e.g., race condition, improper state management).
- Develop a fix or patch to address the issue.
- If necessary, initiate discussions with the validator community to reach social consensus on how to proceed.
- Implement the agreed-upon solution and monitor the network closely during and after the fix.